
Analysis of microvascular network remodeling in ischemic mouse brains
Understanding brain vasculature is crucial for advancing the knowledge of brain functio as the brain consumes a significant portion of energy supplied exclusively through the vascular system. Neurovascular coupling, the relationship between neuronal activity and blood flow dynamics, plays a pivotal role in regulating brain function and is implicated in various neurological disorders, including stroke. Furthermore, ischemic stroke results not only in significant loss of blood vessels but also in severe damage in blood-barrier integrity causing inflammatory processes leading to secondary damage. Light sheet microscopy enables high-resolution imaging of the entire cerebral vascular system. Recently developed automatic analysis tools already allow a fast and precise quantification of vascular topology in specific regions of interest. Further projects are focusing of the analysis of whole brain vasculature including topological details. Moreover, we aim to examine the spatial relationship between blood vessels and other cell types under both normal and pathological conditions. Additionally, we seek to explore alterations in blood flow dynamics during acute and chronic phases following cerebral ischemia.
To achieve this, we are collaborating with experienced biomedical informaticians and specialists in computational analysis, as well as artificial intelligence (AI).
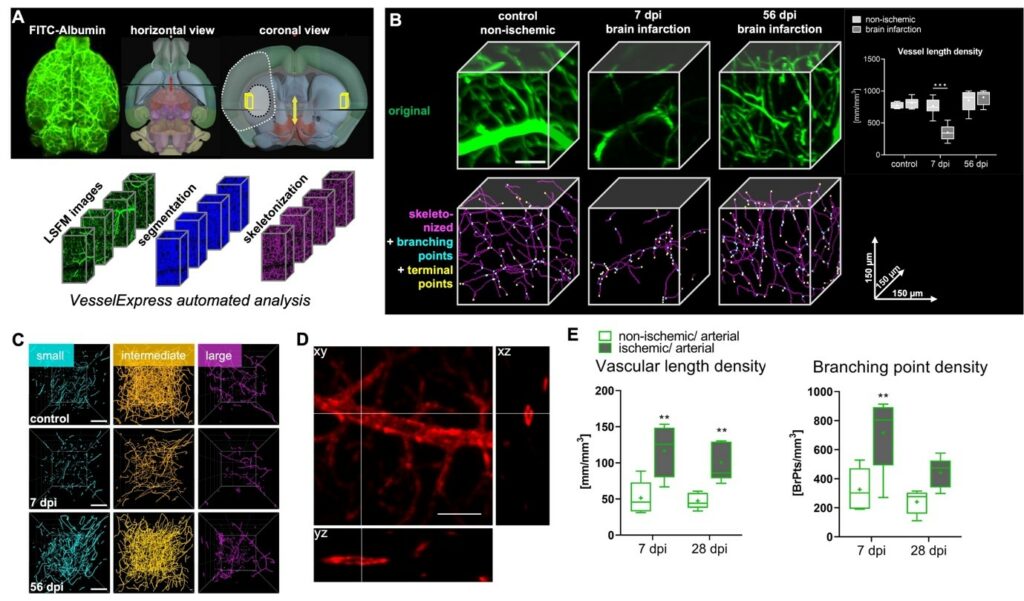
Figure 1: Overview of Microvascular networks analysis tools. A horizontal overview of a mouse brain labeled with FITC-albumin hydrogel (left), or brain topology (middle). Coronal overview (right) displays injured tissue after mild ischemic injury (dark grey dashed line) or brain infarction. Yellow rectangle represents region of interest which can be analyzed using Vessel Express. B Representative original 3D LSFM images (top, in green) or skeletonized graphs (bottom, in magenta; showing branching points, in cyan and terminal points, in yellow) in the dorsolateral ischemic striatum of a control mouse (left), or mice at 7 dpi (center) or 56 dpi examined by VesselExpress. Note the recovery of microvessels at 56 dpi compared with non-ischemic control tissue. Scale bar, 50 µm. C Microvessel skeletons were categorized according to vessel diameters as small (<4 µm diameter, cyan), intermediate (4-5.4 µm, orange) or large (>5.4 µm, magenta) microvessels. Note that MCAO results in the loss of small and intermediate microvessels at 7 dpi, whereas small microvessels increased above non-ischemic at 56 dpi. Scale bars, 100 µm. D orthogonal views (xz and yz) of an artery stained with anti-smooth muscle actin antibody shows hollow vessels which cannot be segmented and skeletonized using original version of VesselExpress. Scale bar, 50 µm E A machine learning model was developed to achieve a filling algorithm followed by VesselExpress analysis. Results show an early re-appearance of arteries 7 days post ischemia (dpi).
Publications
Hagemann, N., Qi, Y., Mohamud Yusuf, A., Li, A., Squire, A., Tertel, T., Giebel, B., Ludewig, P., Spangenberg, P., Chen, J., et al. (2024). Microvascular Network Remodeling in the Ischemic Mouse Brain Defined by Light Sheet Microscopy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.320339.
Spangenberg, P., Hagemann, N., Squire, A., Förster, N., Krauß, S.D., Qi, Y., Yusuf, A.M., Wang, J., Grüneboom, A., Kowitz, L., et al. (2023). Rapid and fully automated blood vasculature analysis in 3D light-sheet image volumes of different organs. Cell Reports Methods. 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100436.
Mohamud Yusuf, A., Hagemann, N., Schulten, S., Rausch, O., Wagner, K., Hussner, T., Qi, Y., Totzeck, M., Kleinschnitz, C., Squire, A., et al. (2020). Light Sheet Microscopy Using FITC-Albumin Followed by Immunohistochemistry of the Same Rehydrated Brains Reveals Ischemic Brain Injury and Early Microvascular Remodeling. Front Cell Neurosci 14, 625513. 10.3389/fncel.2020.625513.







